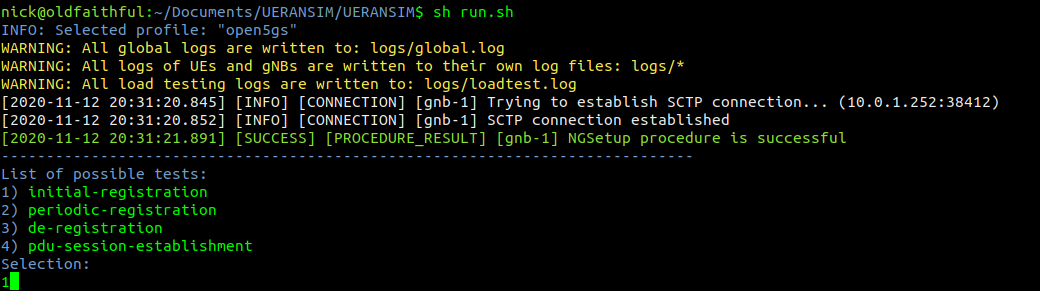
Note: As this space develops so quickly I’ve refreshed the original post from November 2021 in March 2021 with updated instructions.
While 5G SA devices are still in their early stages, and 5G RAN hardware / gNodeBs are hard to come by, so today we’ll cover using UERANSIM to simulate UEs and 5G RAN, to put test calls through our 5GC.
Bringing your 5G Core Online
We’ll use Open5Gs for all the 5GC components, and install on any recent Ubuntu distribution.
Installation is nice and easy;
$ sudo apt update$ sudo apt install software-properties-common$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:open5gs/latest$ sudo apt update$ sudo apt install open5gs
The first point of contact we’ll need to talk about is the AMF,
The AMF – the Access and Mobility Function is reached by the gNodeB over the N2 interface. The AMF handles our 5G NAS messaging, which is the messaging used by the UEs / Devices to request data services, manage handovers between gNodeBs when moving around the network, and authenticate to the network.
By default the AMF binds to a loopback IP, which is fine if everything is running on the same box, but becomes an issue for real gNodeBs or if we’re running UERANSIM on a different machine.
This means we’ll need to configure our AMF to bind to the IP of the machine it’s running on, by configuring the AMF in /etc/open5gs/amf.yaml, so we’ll change the ngap addr to bind the AMF to the machine’s IP, for me this is 10.0.1.207,
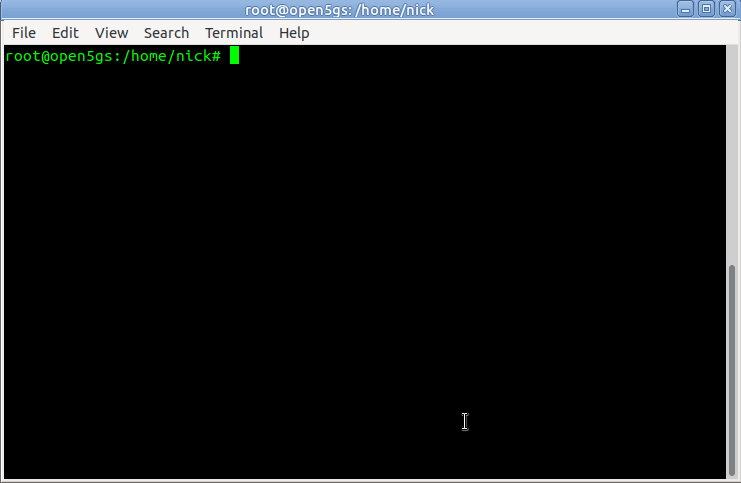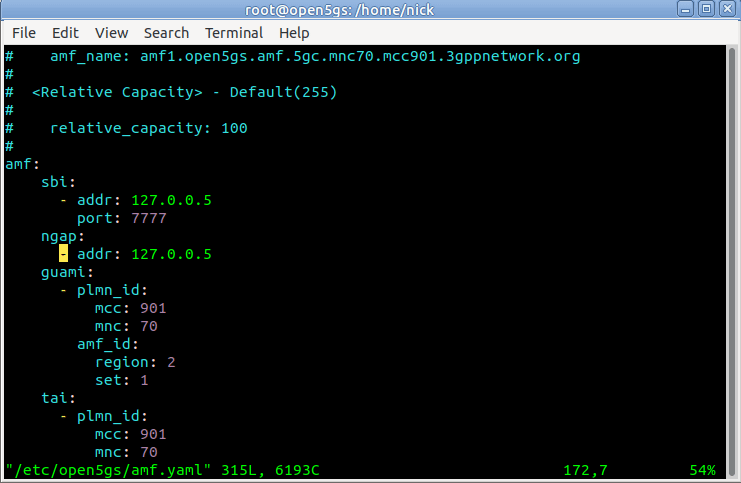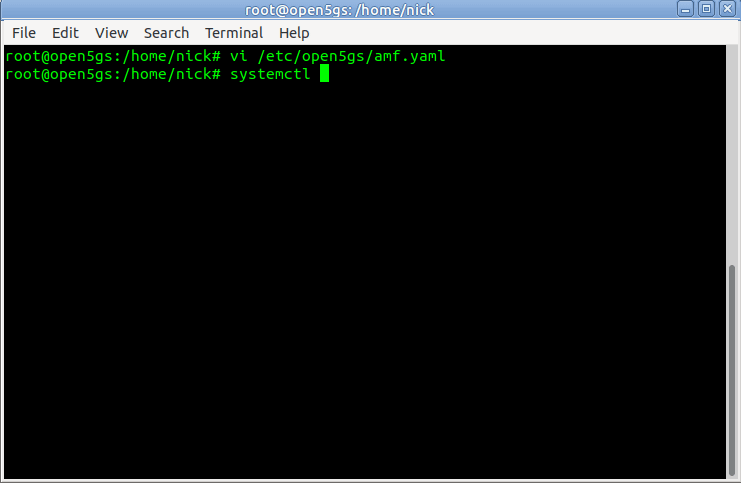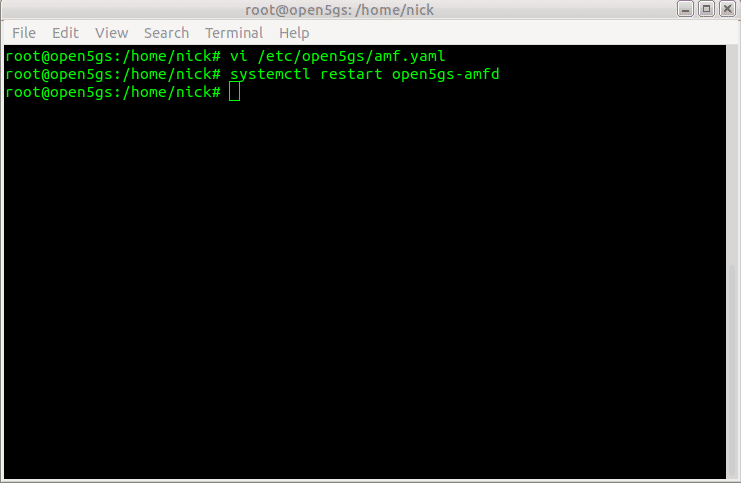
ngap:
- addr: 10.0.1.207In the amf.conf there’s a number of things we can change and configure; such as the PLMN and network name, the NRF parameters, however for now we’ll keep it simple and leave everything else as default.
To allow the changes to take effect, we’ll restart the Open5GS AMF service to make our changes take effect;
$ sudo systemcl restart open5gs-amfd
Setting up the Simulator
We’re using UERANSIM as our UE & RAN Simulator, so we’ll need to get it installed. I’m doing this on an Ubuntu system as we’re using Snaps.
$sudo apt update$sudo apt upgrade$$sudo apt install make g++ libsctp-dev lksctp-toolsiproute2 sudo snap install cmake --classic
With all the prerequisites installed we’ll clone the Git repository and make everything from source;
We’ll clone the Github repository, move into it and make from source.
$git clone https://github.com/aligungr/UERANSIM$cd UERANSIM$make
Now we wait for everything to compile,

Once we’ve got the software installed we’ll need to put together the basic settings.
Running the Simulator (UERANSIM)
UERANSIM has two key parts, like any RAN,
The first is the gNodeB, that connects to our AMF and handles subscriber traffic over our (simulated) radio link,
The other is our subscribers themselves – the UEs.
Both are defined and setup through config files in the config/ directory,
Configuring & Starting the gNodeB
While we’re not actually going to bring anything “on air” in the RF sense, we’ll still need to configure and start our gNodeB.
All the parameters for our gNodeB are set in the config/open5gs-gnb.yaml file,
Inside here we’ll need to set the the parameters of our simulated gNodeB, for us this means (unless you’ve changed the PLMN etc) just changing the Link IPs that the gNodeB binds to, and the IP of the AMFs (for me it’s 10.0.1.207) – you’ll need to substitute these IPs with your own of course.
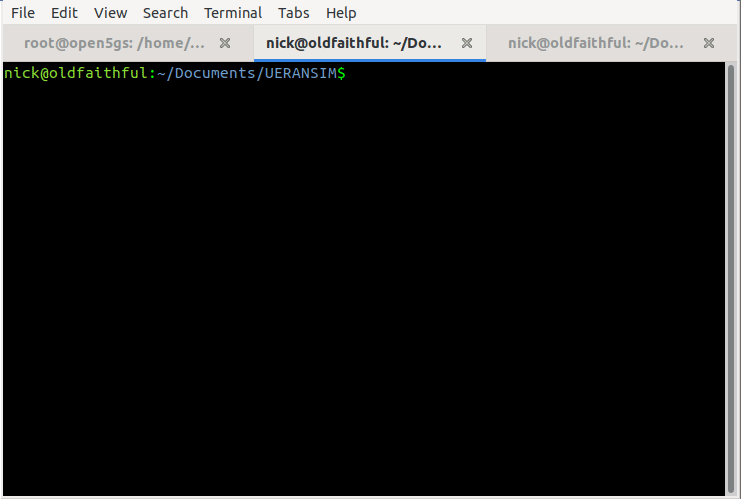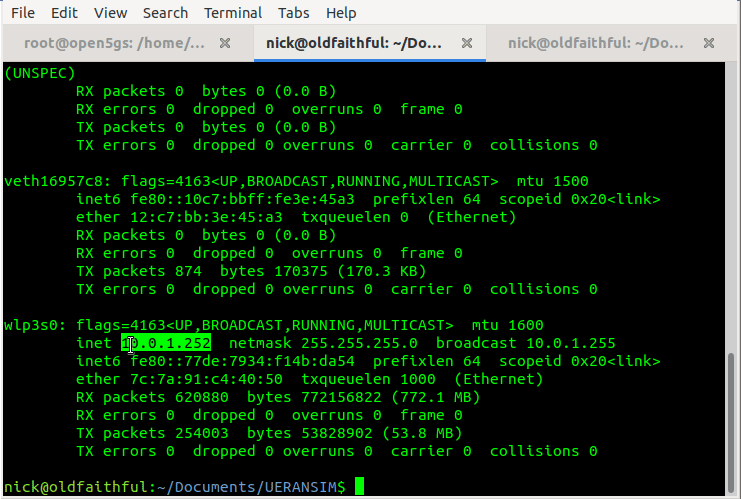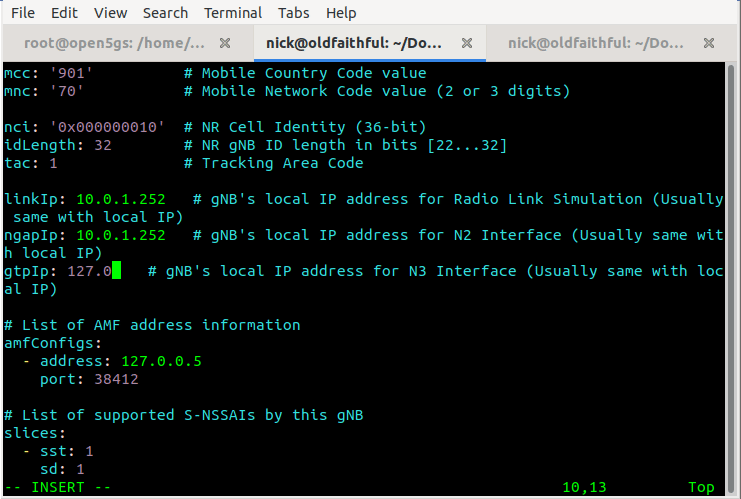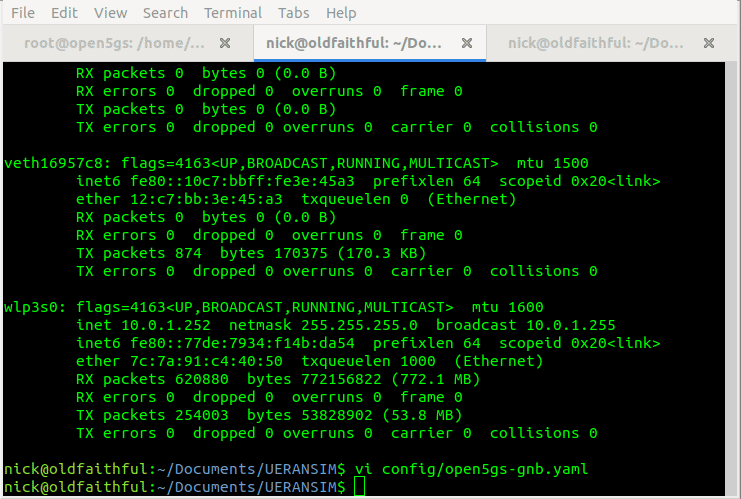
Now we should be able to start the gNodeB service and see the connection, let’s take a look,
We’ll start the gNodeB service from the UERANSIM directory by running the nr-gnb service with the config file we just configured in config/open5gs-gnb.yaml
$ build/nr-gnb -c config/open5gs-gnb.yaml
All going well you’ll see something like:
[2021-03-08 12:33:46.433] [ngap] [info] NG Setup procedure is successful
And if you’re running Wireshark you should see the NG-AP (N2) traffic as well;
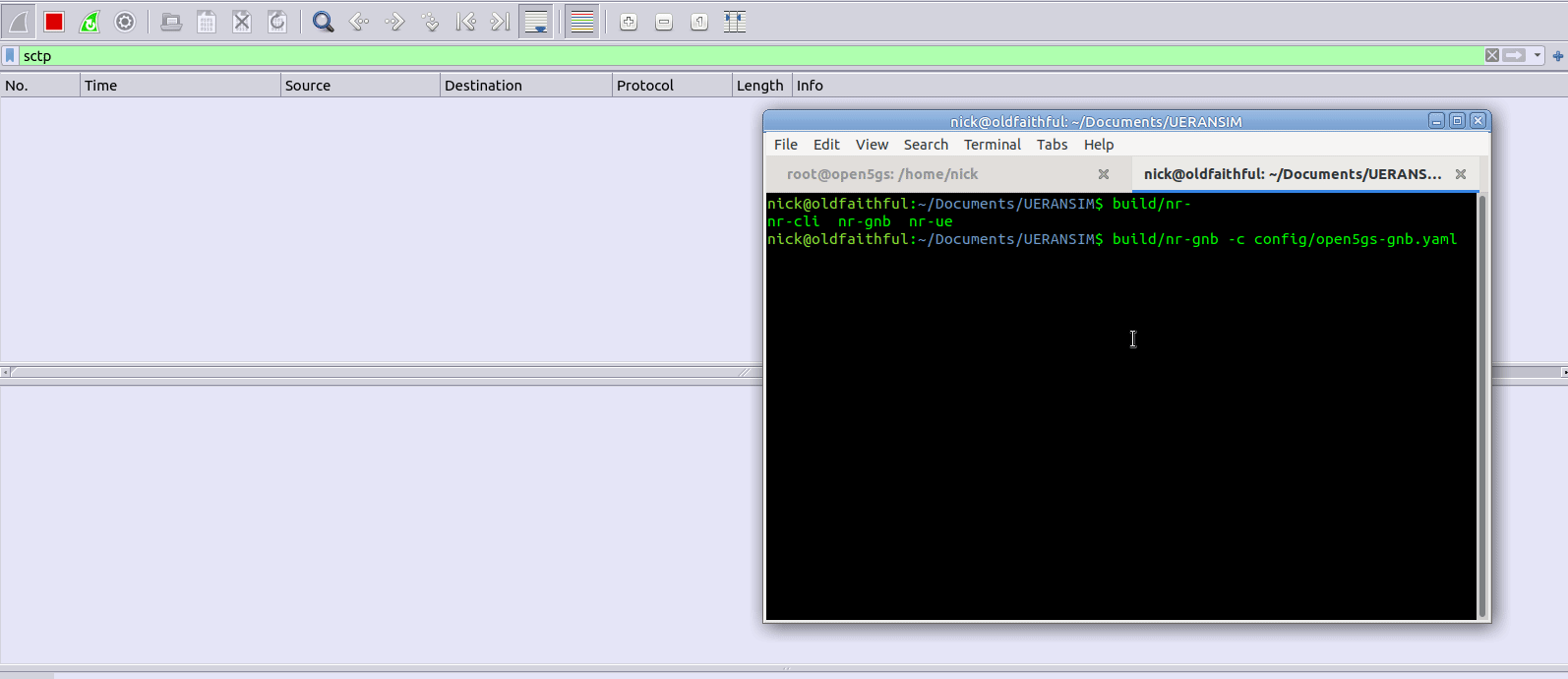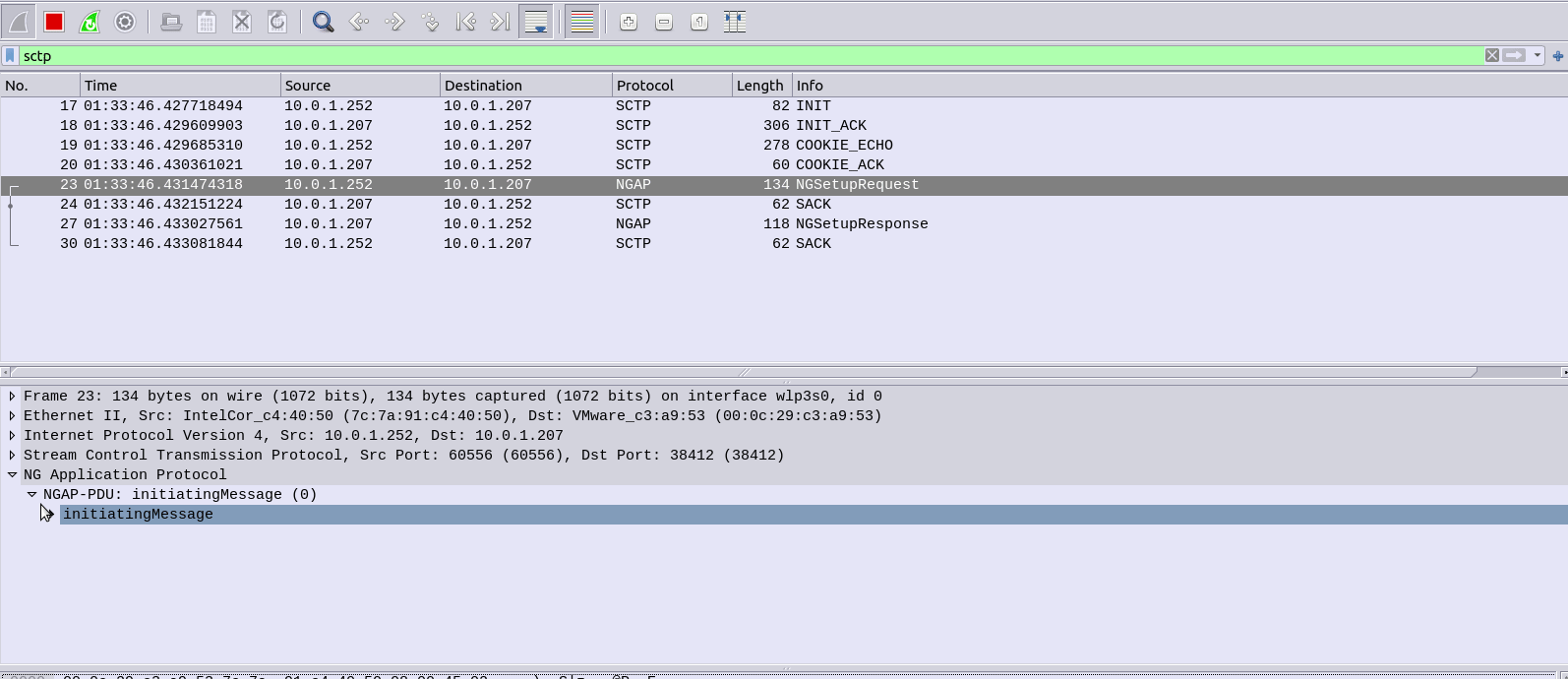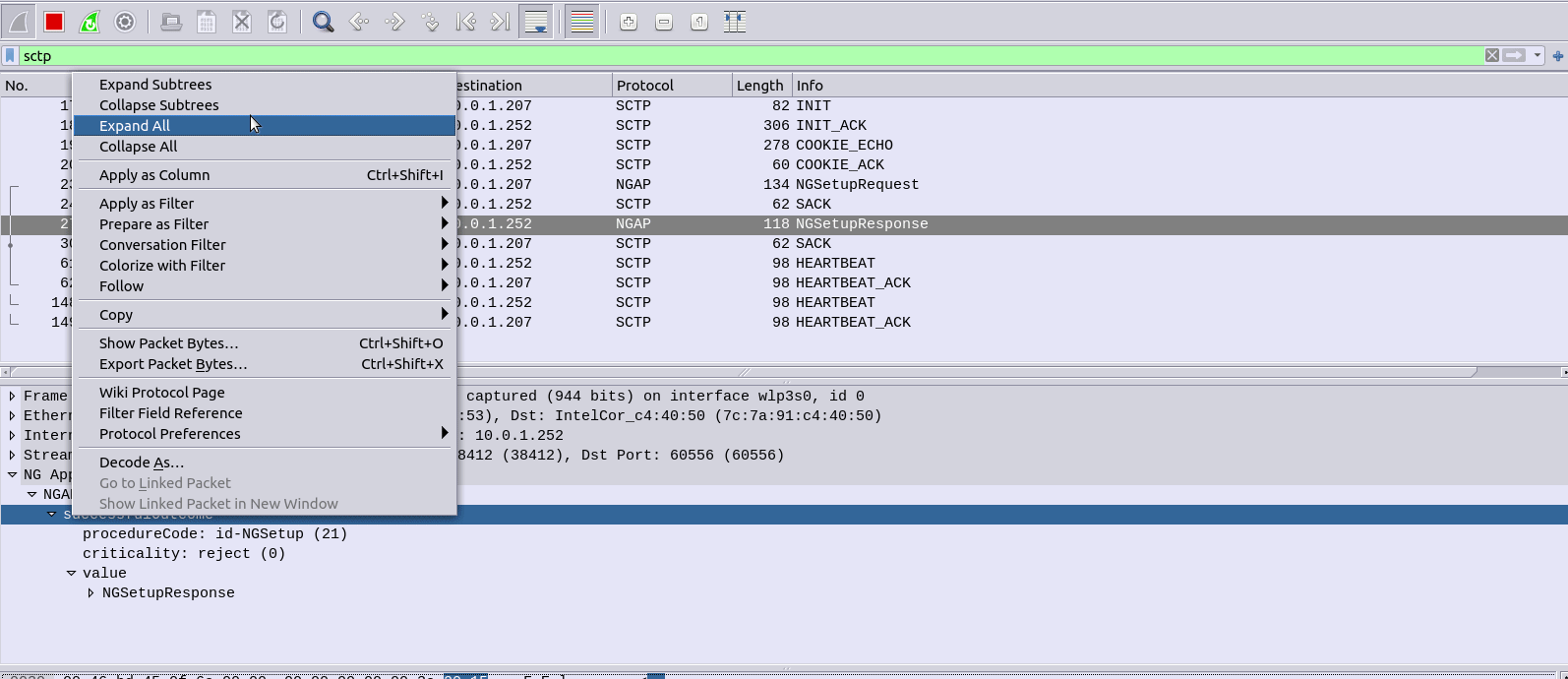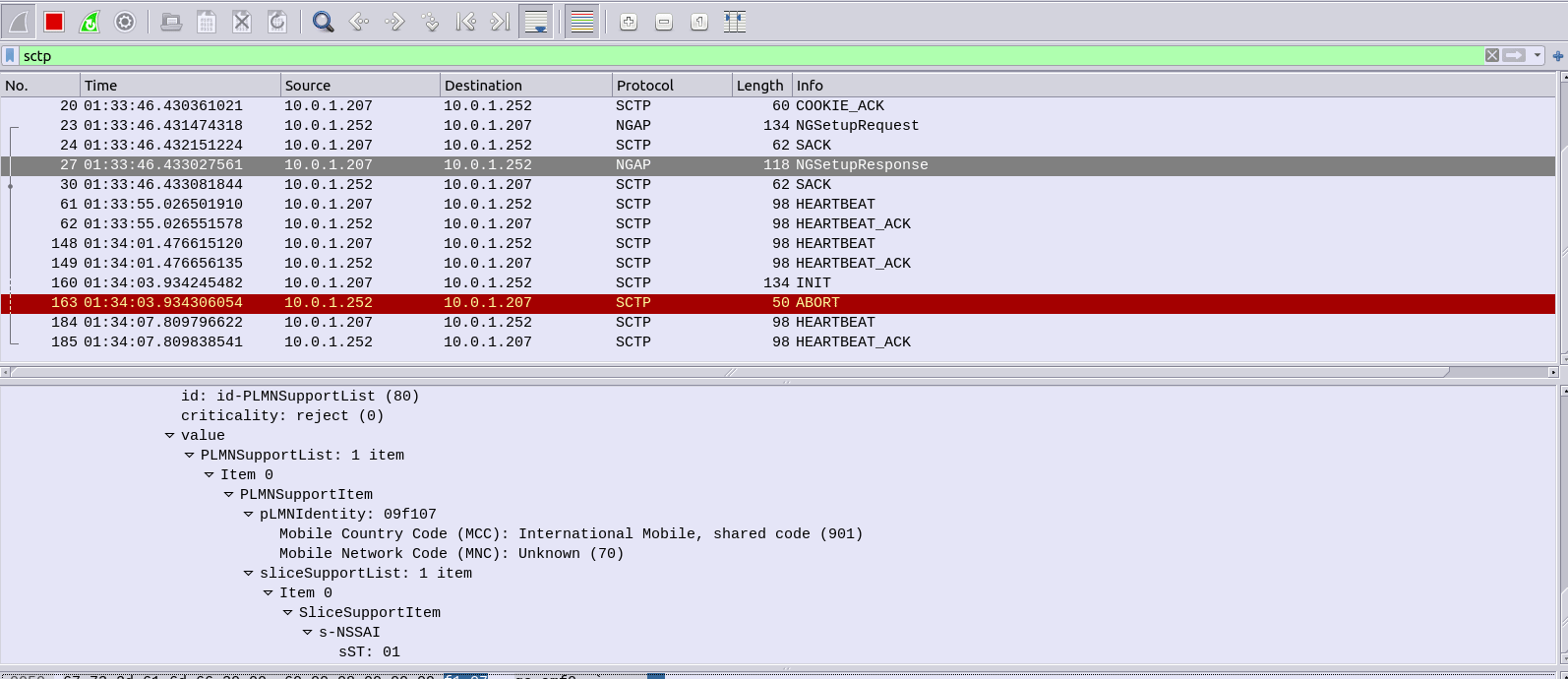
If we tail the logs on the Open5GS AMF we should also see the connection too:
Configuring the UE Simulator
So with our gNodeB “On the air” next up we’ll connect a simulated UE to our simulated gNodeB.
We’ll leave the nr-gnb service running and open up a new terminal to start the UE with:
$ build/nr-gnb -c config/open5gs-gnb.yaml
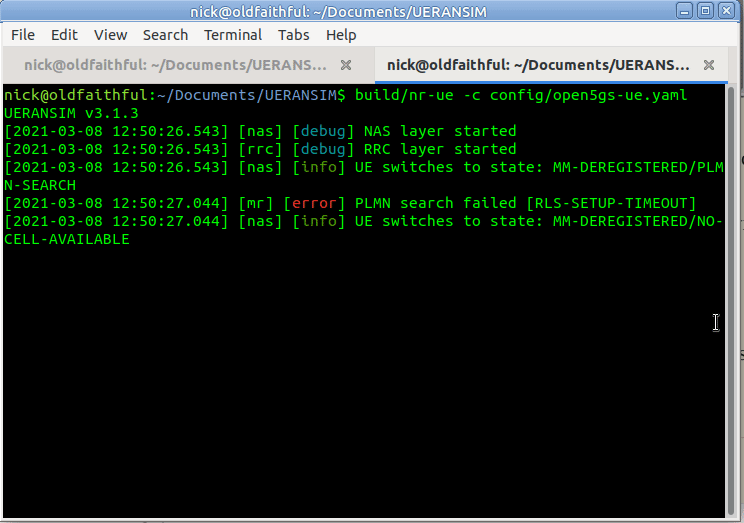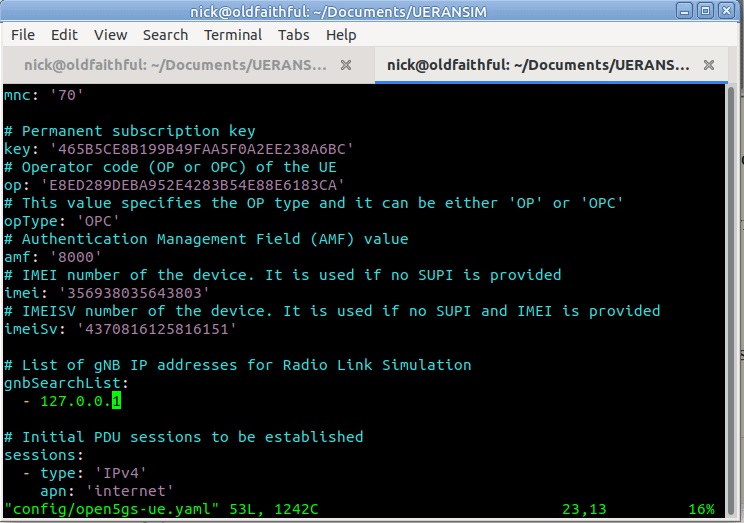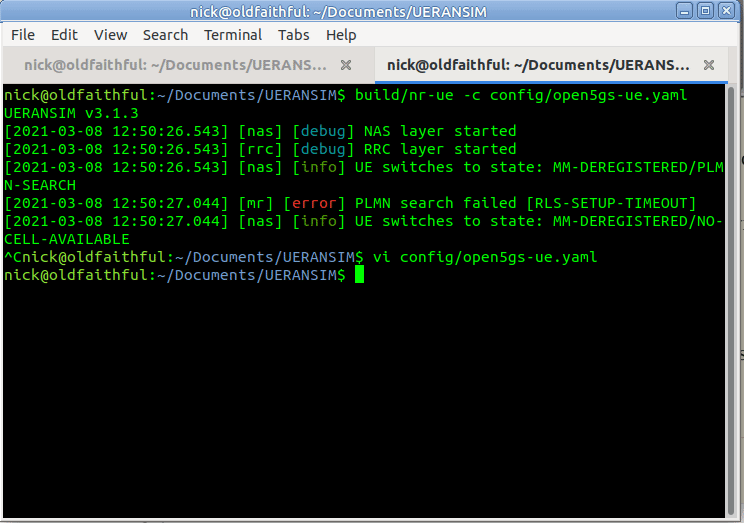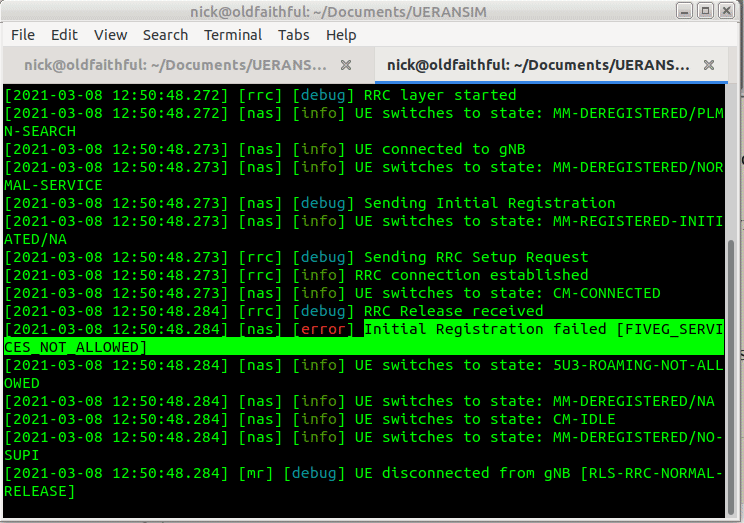
But if you run it now, you’ll just see errors regarding the PLMN search failing,
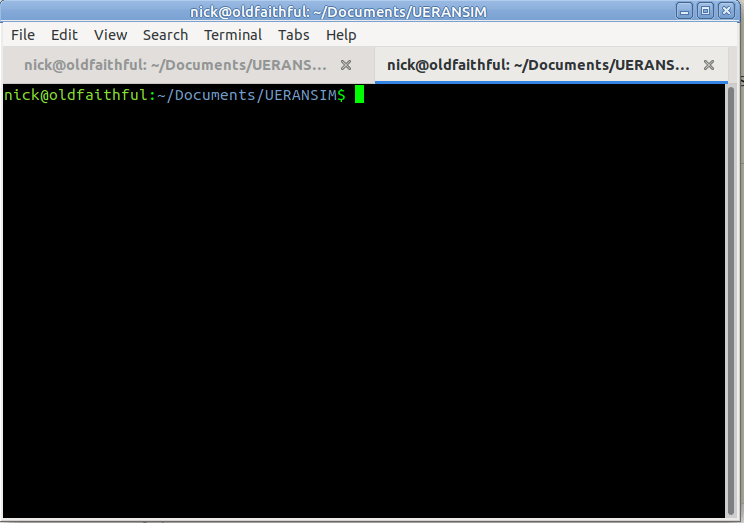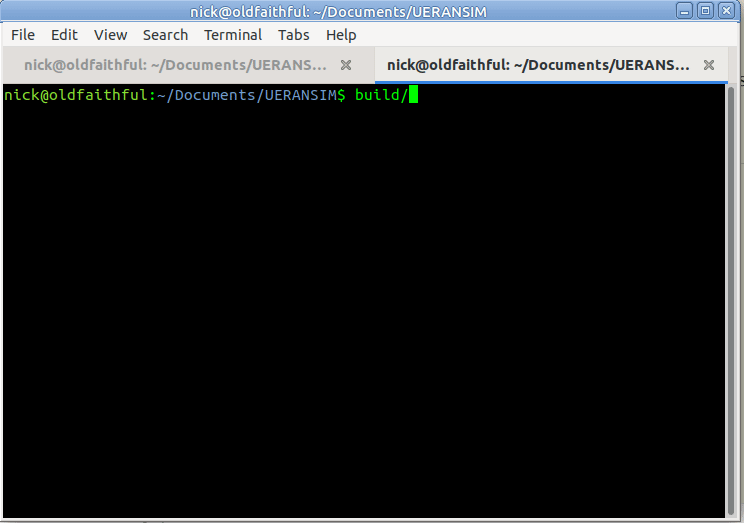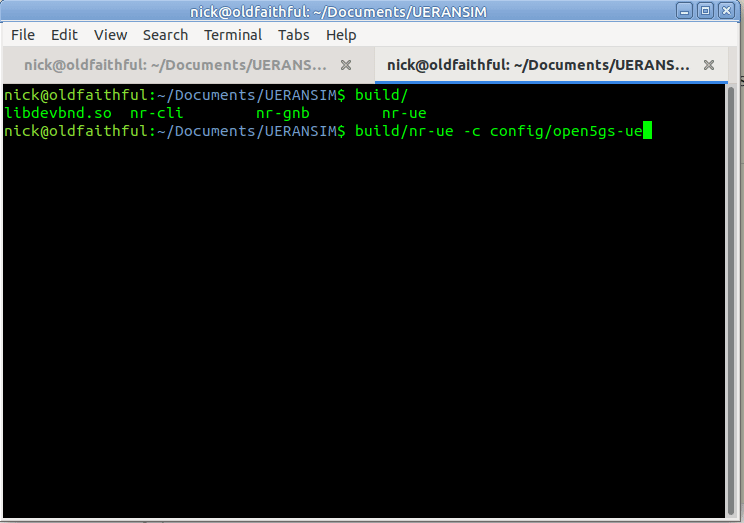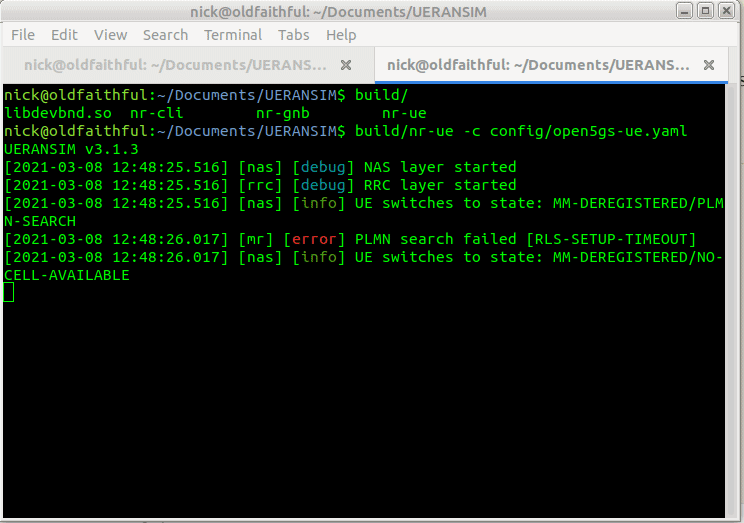
So why is this? We need to tell our UE the IP of the gNodeB (In reality the UE would scan the bands to find a gNB to serve it, but we’re simulating hre).
So let’s correct this by updating the config file to point to the IP of our gNodeB, and trying again,
So better but not working, we see the RRC was released with error “FIVEG_SERVICES_NOT_ALLOWED”, so why is this?
A quick look at the logs on Open5Gs provides the answer,
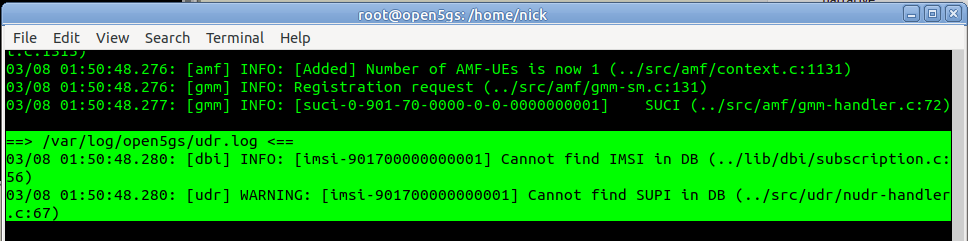
Of course, we haven’t configured the subscriber in Open5Gs’s UDM/UDR.
So we’ll browse to the web interface for Open5GS HSS/UDR and add a subscriber,
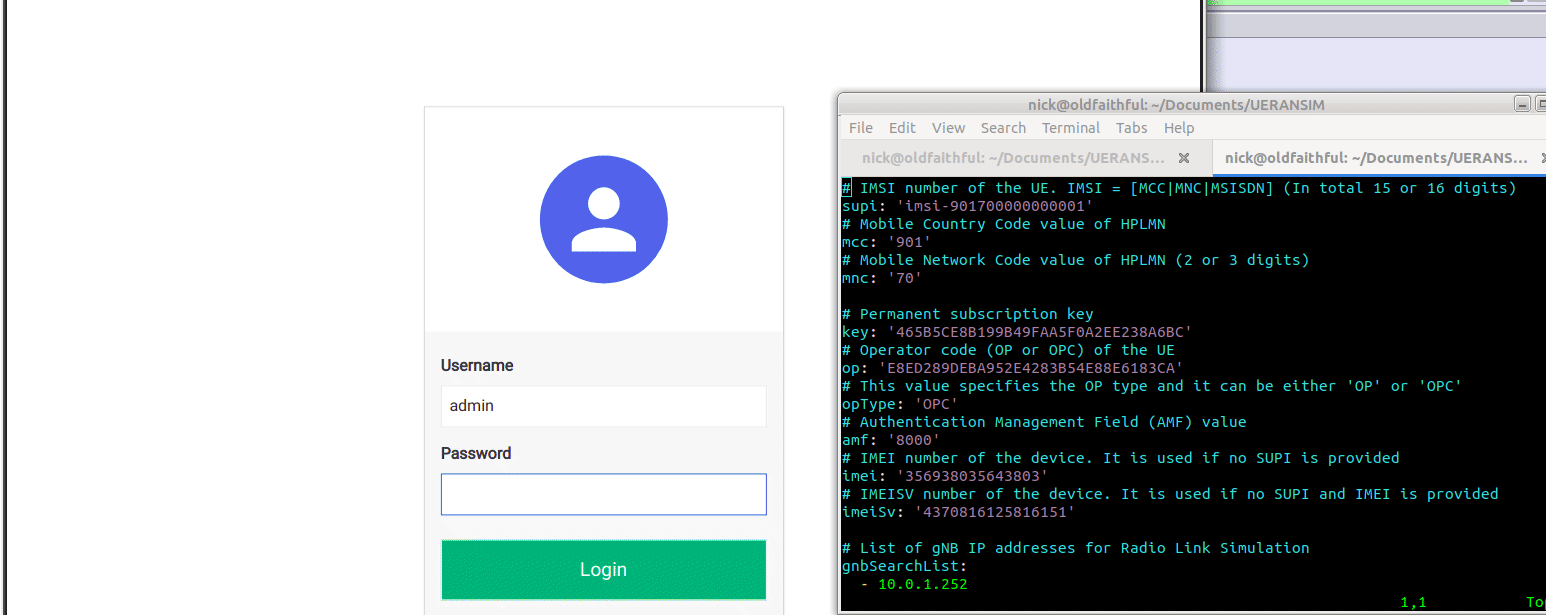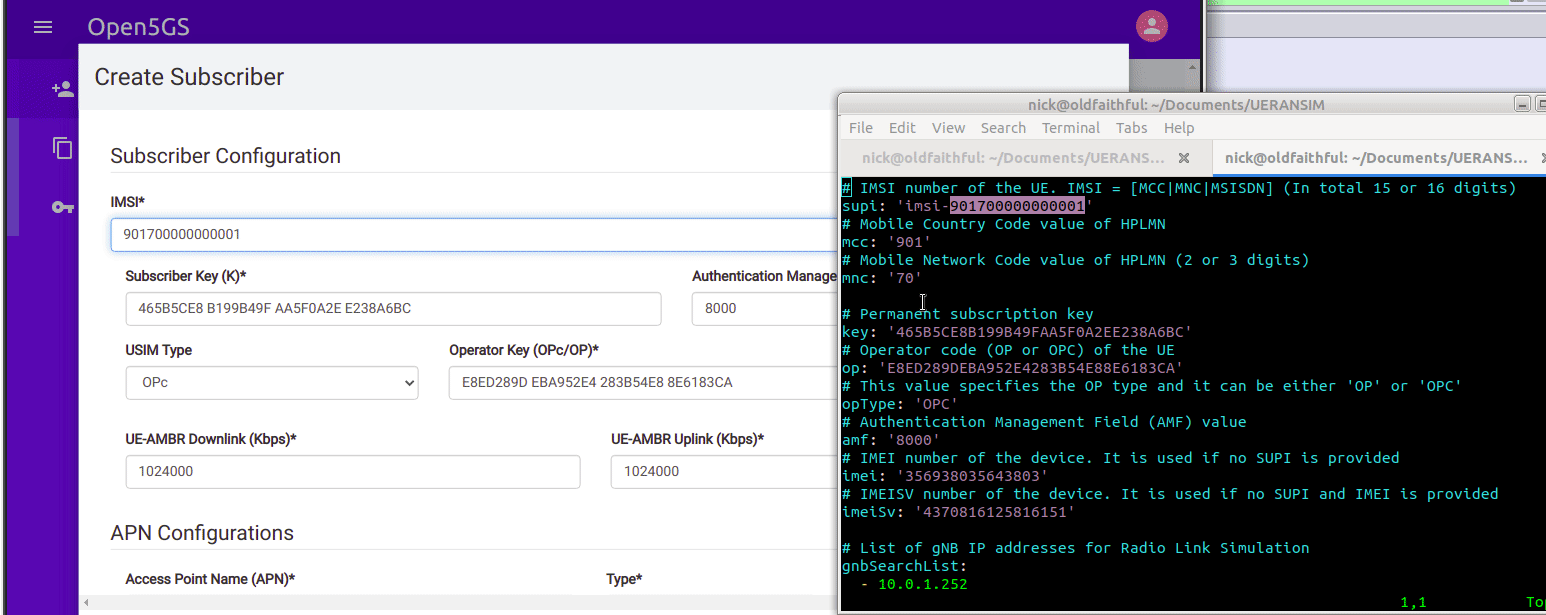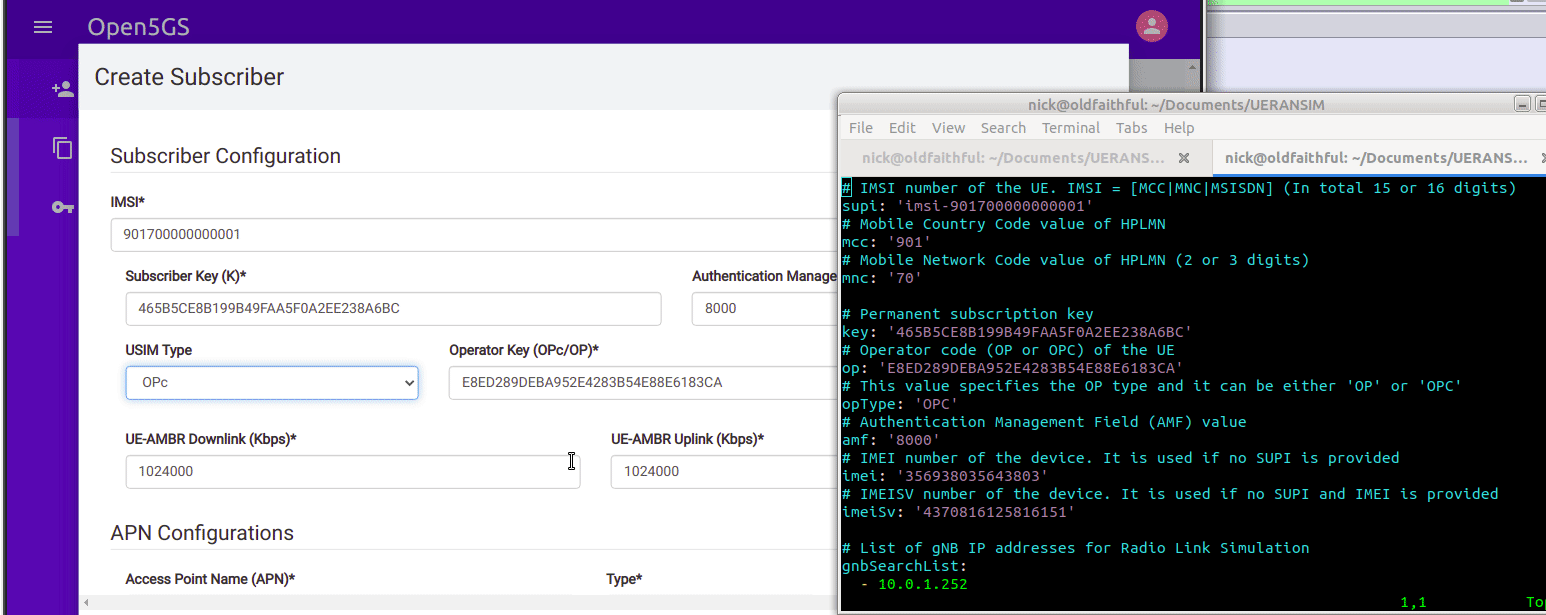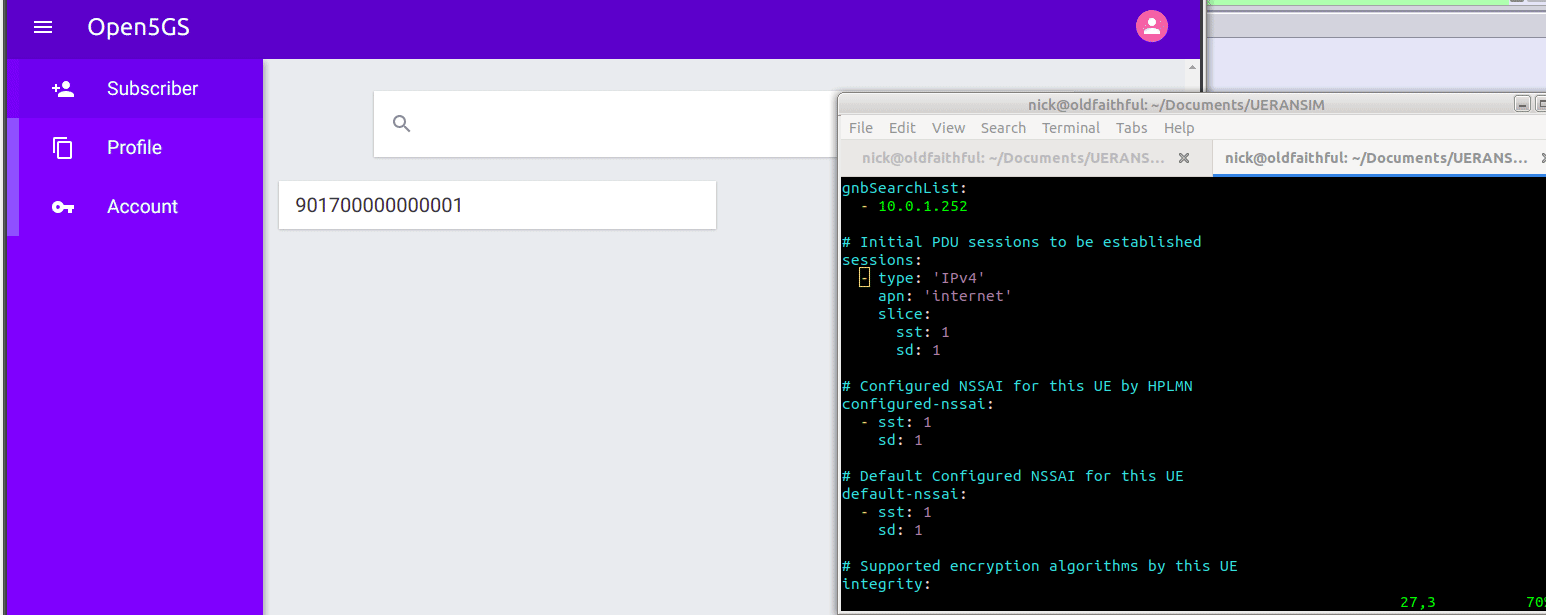
We’ll enter the IMSI, K key and OP key (make sure you’ve selected OPc and not OP), and save. You may notice the values match the defaults in the Open5GS Web UI, just without the spaces.
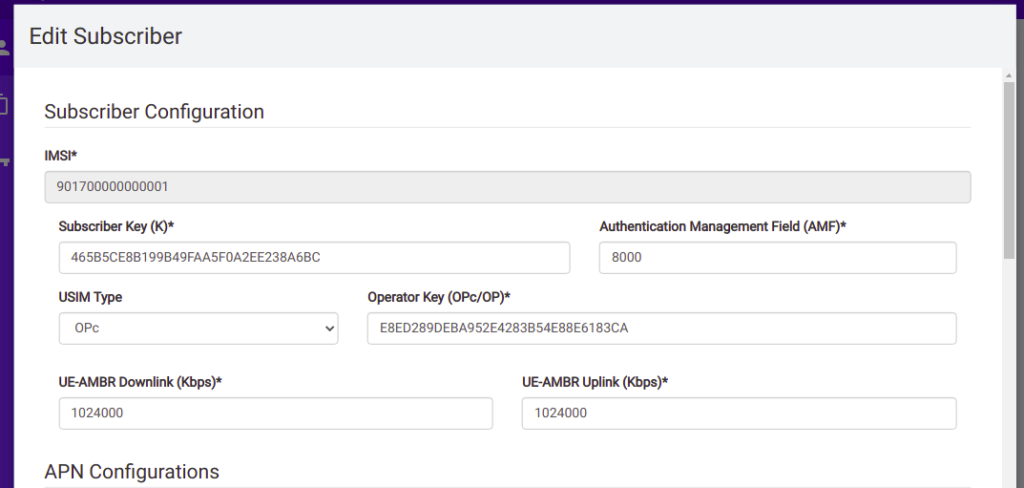
Running the UE Simulator
So now we’ve got all this configured we can run the UE simulator again, this time as Sudo, and we should get a very different ouput;
$ build/nr-gnb -c config/open5gs-gnb.yaml
Now when we run it we should see the session come up, and a new NIC is present on the machine, uesimtun0,
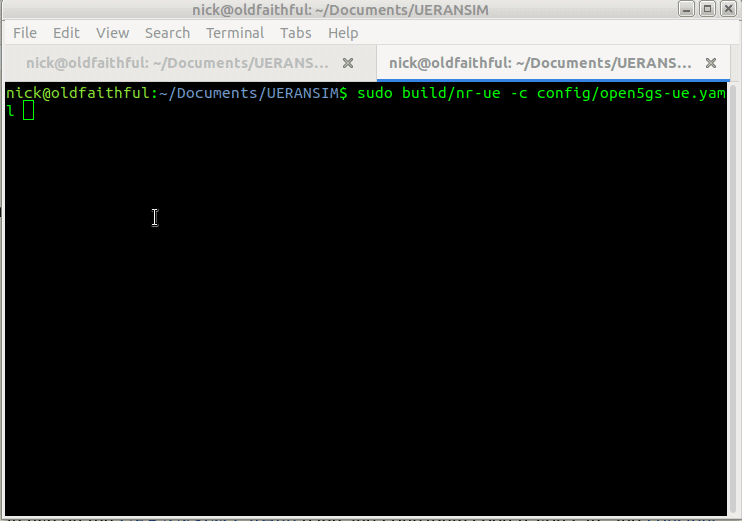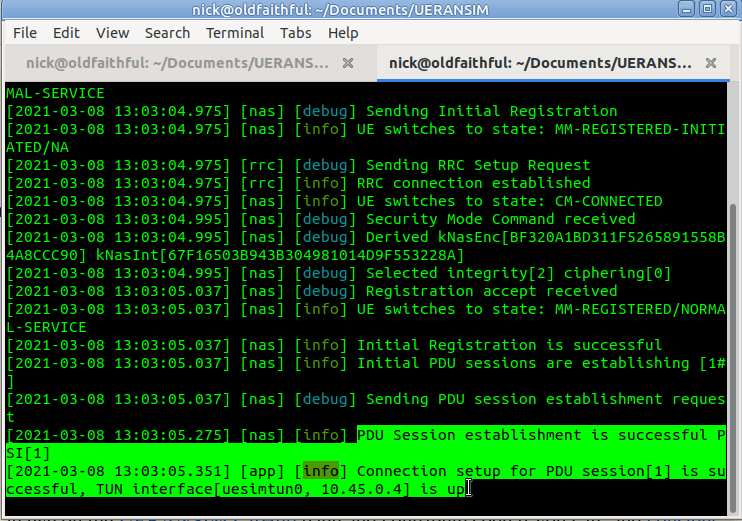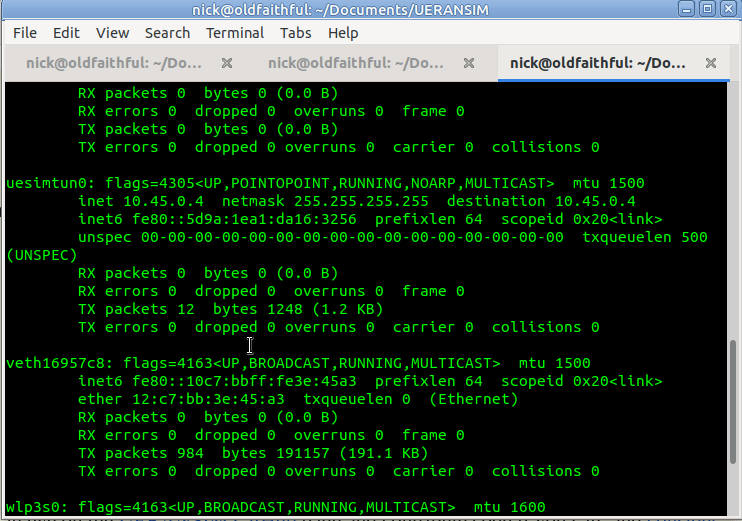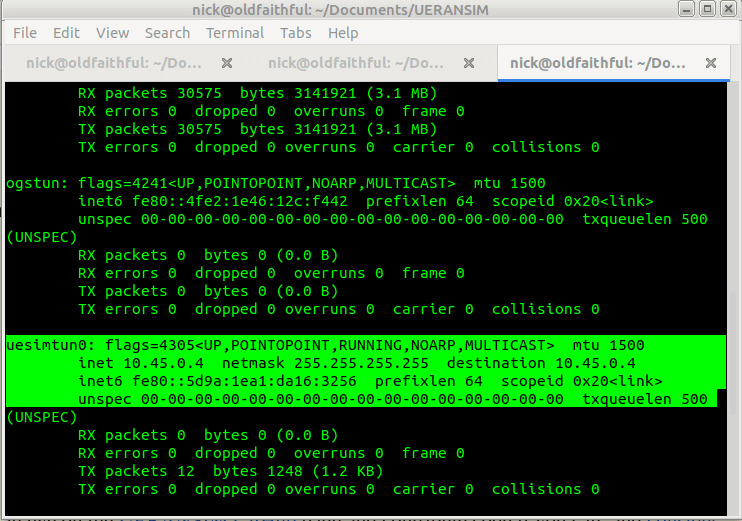
We can now run commands like Ping and Curl and by specifying our special uesimtun0 interface, and the traffic will be encapsulated in GTP and pop out the other end.
Supporting UERANSIM
More advanced functionality is in the works though, so keep an eye on the UERANSIM GitHub page and contribute code if you can, and consider supporting them on Patreon if you can’t, they’re doing great work.